In this blog, I am going to explain the fundamentals of joint actions and muscle contractions, in 3 simple learning points.
You’ll learn:
- Why FitPros find the sliding filament theory so hard to revise
- The link between joint actions and muscle contractions
- What are flexion and extension?
- The importance of understanding muscle fibre direction
- What are concentric and eccentric muscle contractions
- How to unpick complicated exam questions
- How to learn with simplicity for the rest of the modules
- Three Example Mock Questions about joint actions
Why FitPros find Joint Actions so hard to revise
Learning Joint Actions and Muscle Contractions are notoriously claimed to be one of the hardest modules within the Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology syllabus, so you are not alone if you find this area difficult to understand.
Although we can see and feel our joints move, it can be hard to link the names of all joint actions and understand the different types of muscle contractions.
You can expect between 5 and 8 questions relating to this in your Level 3 Anatomy exam
Often we see learners over-complicate the joint actions and muscles contractions by trying to remember the smallest detail first, even before learning the foundations.
That’s why I’m going to simplify it with these fundamental 3 learning points:
Joint Actions and Muscle Contractions: The fundamentals
1. What is Flexion and Extension?
You need to know 17 joint actions for your Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology exam. However, starting with the fundamentals, you definitely need to know the difference between Flexion and Extension.
All of our joints are in extension when we stand in a neutral position, with palms facing forwards.
All of our joints are in extension when we are in a foetal position – except shoulders which are in full flexion when arms are overhead.
So here is a memory hack to help you decipher between the two:
Extension = Elongated in Neutral position
Flexion = Foetal Position (+arms overhead)
Watch the video to get a clear visual
To learn all 17 joint actions alongside all of the information required to pass your exam, check out our Level 3 Revision Mastery Bootcamp:
https://courses.parallelcoaching.co.uk/products/level-3-anatomy–physiology-revision-bootcamp
2. Understand Muscle Fibre Direction
It is crucial to have a good understanding of the muscle fibre direction of each muscle, these are the striations that run from one end of a muscle to the other.
If you know what way the muscle fibre runs, then you can predict the joint action it creates.
Imagine the striations are a tug of war rope, with a team sat on each attachment point.
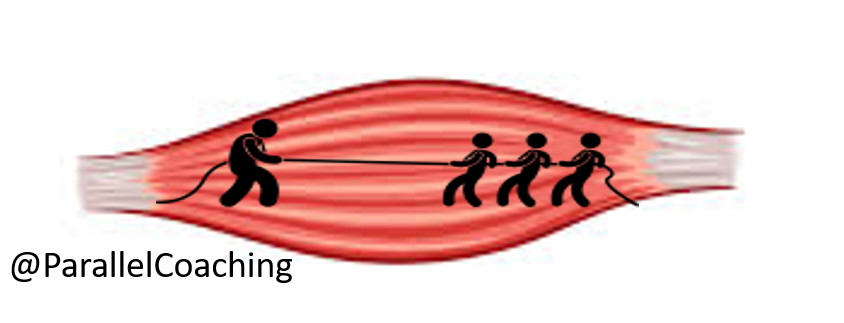
When the muscles contract, when they shorten and lengthen they lengthen along the direction of the muscle fibre striations.
If you are looking for clear images of the muscles, then check out our muscle memory flashcards, including all of the origins, insertions and joint actions CLICK HERE
3. What are Concentric & Eccentric Contractions?
Most people think of muscle contraction as muscle shortening. However, there are 2 types of contractions for each muscle, one that gets longer and one that gets shorter.
You need to know that a concentric contraction is muscle shortening,
… and eccentric contraction is muscle lengthening.
You can remember this using…
Concentric = Collapsing (shorter)
Eccentric = Elongating (longer)
Test your knowledge with today’s mock questions:
[NOTE: The answers are below the 3rd question]
1. Which joint action occurs when the rectus abdominus contracts concentrically?
A – Hip Extension
B – Hip Flexion
C – Spine Flexion
D – Spine Extension
2. What joint action happens when the Biceps Brachii contracts eccentrically?
A. Elbow Flexion
B. Elbow Extension
C. Shoulder Adduction
D. Elbow Lateral Flexion
3. Knee Extension occurs when which muscle contracts concentrically?
A. Hamstrings
B. Iliopsoas
C. Quadriceps
D. Adductors
What’s the CORRECT answer?
Answers to the mock questions are :
Question 1= C, Question 2 = B, Question 3 = C
If you want more mock questions like this, then you can download more Free Mock Questions: DOWNLOAD NOW
Need More Help with your Level 3 Anatomy Revision?
For Trainee FITPROS Taking Their L3 Anatomy & Physiology Exam.
Learn, Revise & Pass Your Level 3 Anatomy & Physiology Exam In Under 10-hours
(Without Having To Spend Hours Revising Or Feeling Overwhelmed)
If you want to get your revision structured, learn everything you need to know, and feel confident on exam day, then click the link below:

Dedicated to More
Hayley “Joint Actions and muscle contractions” Bergman
Parallel Coaching
P.S. You can also find us on the following platforms:
Instagram: Follow Now
Facebook: Like Our Page
Twitter: Tweet Us
YouTube: Subscribe Here
More Anatomy Revision Blogs: HERE

