What are the three types of muscles in the body? Though it may seem like a simple question, this blog post will explore what the three types of muscles are and how they differ.
The three types of muscle that we discuss today include cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, and smooth muscle. We’ll go into detail about what these all mean below!
In this blog and video, we will explore the characteristics of the Three Types Of Muscles In The Body. The 7-minute video will also provide examples and explore the function of each type in preparation for your level 2 and level 3 anatomy exam
What Are the Three Types Of Muscles In The Body?
There are three types of muscles in the body:
- Skeletal
- Cardiac
- Smooth
Why do I need to know Three Types Of Muscles In The Body?
You will need to understand each of these muscle types, their characteristics, and examples for your Level 2 and Level 3 anatomy exam. You can expect 3-8 questions that relate to musculoskeletal system content, including understanding how muscles contract, the sliding filament theory and the types of muscles
Knowing the three types of muscles will also help compound your knowledge in other areas of anatomy and physiology, including digestive system and the heart and circulatory system.
As a FITPRO or personal trainer, you need to know that not all muscle in the body is the same, and those we use for exercise are different to those in our digestive tract, arteries or heart muscle (myocardium).
WATCH: What Are the Three Types Of Muscles In The Body?
Let’s take an in-depth look at each of these three muscle types in the body and examples
The three major types of muscles in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and help with movement. Smooth muscles control blood flow throughout the body while cardiac muscle is responsible for pumping blood through your heart.
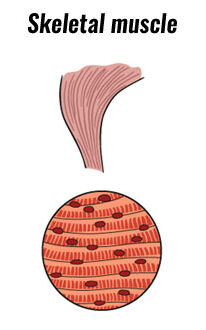
What is Skeletal Muscle?
Characteristics = Voluntary and Striated.
Skeletal muscle is found in the body and controls movement. These muscles are striated, which means they look striped when pulled or viewed under a microscope.
These striations are a result of the muscle fibres that run from origin to insertion of each skeletal muscle. The sarcomere then divides along the length of the muscle fibre to allow for a forceful contraction in one direction.
These muscles are voluntary, which means that they can be consciously controlled by the brain.
Examples of Skeletal muscle include the biceps and quads.
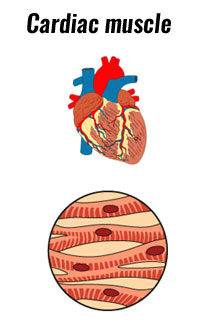
What is Cardiac Muscle?
Characteristics = involuntary and striated
Cardiac muscle is only found in the heart
It is striated tissue like a skeletal muscle and conducts nerve impulses more rapidly than other muscles in the body because it is supplied with a special type of fibre called cardiac fibres.
The myocardium (heart muscle) is involuntary which means it is not under voluntary control, which is important to ensure it beats consistently every minute of every day.
Muscle contraction is triggered by nerve impulses and will contract automatically
The cardiac muscle has a rapid response time to these signals and contracts rapidly, even without the aid of adrenaline or other hormones that affect skeletal muscles’ contractibility. This type of muscle also does not show signs of fatigue during prolonged use (unlike smooth muscle).
This type of muscle varies in thickness depending on the location of the heart and its function. The lower chambers (ventricles) are thicker than the upper chambers.
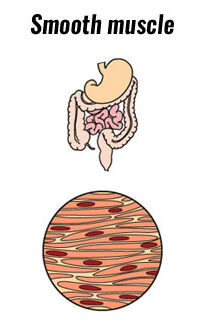
What is Smooth Muscle?
Characteristics = involuntary and smooth
Smooth muscle is found in many places throughout the body and controls involuntary functions such as blood pressure, peristalsis (the process by which food moves through our intestines), and digestion. These muscles are not striated like skeletal muscles because of the thin, seamless appearance that they have.
Instead of a forceful contraction like in striated muscle, smooth muscle contracts along the diameter like in blood vessels that vasoconstrict and vasodilate, which means they constrict and open up.
Smooth muscle is found in many places throughout the body and controls involuntary functions such as blood pressure, peristalsis (the process by which food moves through our intestines), and digestion.
Test your knowledge with 3 Mock Questions
Look at the three Anatomy and Physiology Mock questions below and jot down your answer on scrap paper or as a note in your phone.
Then scroll down to reveal the answers.
1) Which muscle type is responsible vasocontriction of arteries?
A. Smooth
B. Cardiac
C. Skeletal
D. Voluntary
2) What are the characteristics of the muscle type that make up the myocardium?
A. Involuntary and Smooth
B. Voluntary and Smooth
C. Involuntary and striated
D. Voluntary and Striated
3) What gives skeletal muscle a striped look?
A. The smooth muscle
B. The muscle fibres and sarcomeres
C. The chambers
D. The actin and myosin
Answers:
Q1: Answer = A
Q2: Answer = C
Q3: Answer = B
If you want more mock questions like this, then you can download more Free Mock Questions: DOWNLOAD NOW
Need More Help with your Level 3 Anatomy Revision?
For Trainee FITPROS Taking Their L3 Anatomy & Physiology Exam.
Learn, Revise & Pass Your Level 3 Anatomy & Physiology Exam In Under 10-hours
(Without Having To Spend Hours Revising Or Feeling Overwhelmed)
If you want to get your revision structured, learn everything you need to know, and feel confident on exam day, then click the link below:

Dedicated to More
Hayley “What Are the Three Types Of Muscles In The Body?” Bergman
Parallel Coaching
P.S. You can also find us on the following platforms:
Instagram: Follow Now
Facebook: Like Our Page
Twitter: Tweet Us
YouTube: Subscribe Here
More Muscles Blogs: HERE