A common question in the Level 2 anatomy and physiology exam is about blood pooling.
A typical blood pooling question might look like…
In today’s blog, we’ll explore the answer in-depth so you can be confident in your Level 2 anatomy knowledge.
There are 8 topics you must cover in your level 2 anatomy and physiology exam. You can learn about all 8 below. Blood pooling is within topics 1 of 8: The heart and circulation.
Let’s jump straight in and dissect the above level 2 anatomy mock question.
First up, let’s learn and revise more about blood pooling.
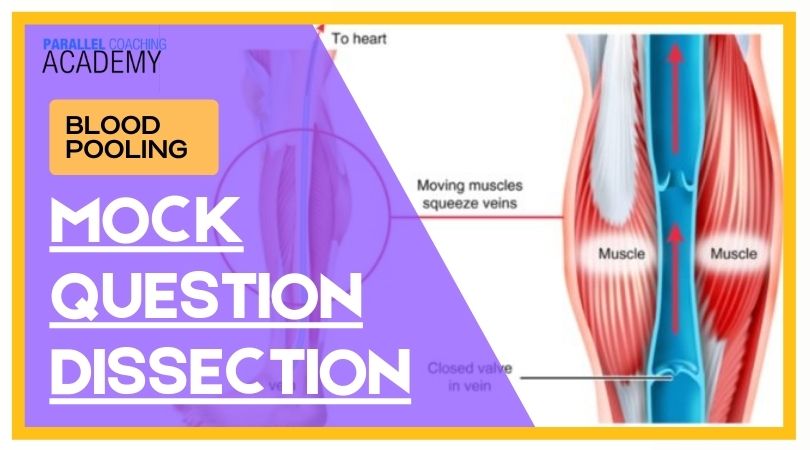
Blood pooling occurs when the blood is unable to pump back up to your heart. Consequently blood pools (or collects) in your legs, ankles, and/or feet.
Now then, blood pooling in feet and legs can happen due to a number of different issues.
Obviously, we are talking about blood pooling and exercise. I’ll also outline some other issues shortly.
But during exercise, we increase cardiac output.
Cardiac output is the term that describes the amount of blood your heart pumps each minute.
Cardiac output = stroke volume × heart rate.
This increase in cardiac output is necessitated by the active muscles’ need for oxygenated-rich blood. For large amounts of blood to be circulated to the active muscles, an equally large amount of blood must be returned.
Blood pooling can occur with rapid cessation (sudden stopping) of exercise due to an inadequate amount of blood returning to the heart.
Let’s dive a little bit deeper…
During exercise, your muscles aid the amount of blood returned to the heart by contracting with more force around the blood vessels.

This causes the blood to easily resist the forces of gravity and return quickly to the heart for re-oxygenation and re-circulation. When you stop exercising quickly, the muscles are no longer contracting against your blood vessels
and gravity causes the blood to pool in the lower extremities.
When this occurs, you may feel faint or dizzy or experience a loss of consciousness.
This is why it’s crucial to learn and implement a safe and effective cooldown.
The purpose of a cool-down after any physical activity is to return your heart to its resting state. This will help avoid blood pooling in the lower extremities. Ultimately the cool-down allows for the working muscles to contribute to venous return.
Remember… exercise is a stressor on the body.
Many physiological occurrences take place as a result of exercise. Both in an acute (immediate) way and prolonged after. It is vital you are aware of these physiological occurrences (aka. Blood pooling) and plan client sessions accordingly.
There are other issues for blood pooling including:
- Being overweight
- Pregnancy
- Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Heart complications
- Family history of the problem
- Had damage to the leg such as injury, surgery, or previous blood clots
Now we know more about what blood pooling is… let’s jump back to the mock question and potential answer to pluck out some keywords.
Which of the following is a direct symptom of blood pooling following sudden cessation of intense exercise?
The question is asking for a direct symptom of blood pooling.
A symptom is something that indicates the existence of something else. This mock question is asking… What can a FITPRO observe in their client that could indicate blood poling might be present.
The 4 possible answers are:
- a. Heart arrhythmias
- b. High blood pressure
- c. Dizziness/feeling faint
- d. Hyperventilation
Let’s find out what we know about the 4 possible answers.
We know we cannot observe a heart arrhythmia. Heart arrhythmia is to do with electrical impulses that coordinate the heartbeat. Plus blood pooling doesn’t cause changes to the heart rate.
We know we cannot observe high blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of circulating blood on the walls of the arteries. A stethoscope or digital blood pressure machine can only be used to ascertain blood pressure. PLus blood pooling doesn’t cause an increase in blood pressure, it is a result of low blood pressure.
We can observe hyperventilation though. Hyperventilation is rapid or deep breathing, usually caused by anxiety or panic. Remember we are concerned with blood pooling, not anxiety or panic.
This over-breathing, as it is sometimes called, may leave you feeling breathless.
When you breathe, you inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide.
Excessive breathing may lead to low levels of carbon dioxide in your blood. This causes many of the symptoms such as:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Belching, bloating, dry mouth
Now here lies some potential confusion for the above mock question.
One of the potential answers… (C) Dizziness/feeling faint can be a symptom of hyperventilation.
Yet the mock question is asking for symptoms of blood pooling.
Once you’ve read the mock question, plucked out the keywords, and explored the potential answers… It’s key to go back to the mock question and remind yourself of what’s being asked.
Making sure you link the question to the right answer.
This way you don’t get sucked into linking a potential answer to something you are not being asked about. After all… dizziness, lightheadedness, and shortness of breath are symptoms of hyperventilation… and are associated with exercise But NOT associated with blood pooling.
All too often trainee fitness peeps refer/fail their final exam… not because of not knowing enough or their knowledge.
Rather they haven’t read the question and potential answers properly.
… and the answer to today’s mock question?
(C) Dizziness/feeling faint
This is a symptom of blood pooling, or in other words blood pooling can cause you to feel dizzy or faint.
Drop a comment below, did you get this question correct?
Top Tips to Pass Your Exam
I have two top tips so you can pass your fitness exams confidently
1) read the question,
read the potential answer, go back and re-read the question
and be sure to link the question and answer together.
Do not link one potential answer with another (1+1 = 3 scenario)
Download Hundreds of Mock Questions For Free
If you want more mock questions like this, then you can download more Free Mock Questions: DOWNLOAD NOW
2) get help to structure your revision and unpick tough questions
Need More Help with your Level 2 Anatomy Revision?
For Trainee FITPROS Taking Their L2 Anatomy & Physiology Exam.
Learn, Revise & Pass Your Level 2 Anatomy & Physiology Exam In Under 10-hours
(Without Having To Spend Hours Revising Or Feeling Overwhelmed)
If you want to get your revision structured, learn everything you need to know, and feel confident on exam day, then click the link below:

Dedicated to More
Hayley “Blood Pooling Mock Questions Dissection” Bergman
Parallel Coaching
P.S. You can also find us on the following platforms:
Instagram: Follow Now
Facebook: Like Our Page
Twitter: Tweet Us
YouTube: Subscribe Here
More Mock Question Blogs: HERE