A common question in the Level 2 anatomy and physiology exam is “What is the Synergist Muscle in the Lying Hamstring Curl?” Here we will explore the answer in-depth so you can be confident in your knowledge.
This mock question is for the level 2 anatomy exam. If you are revising for your level 3 anatomy exam use the below knowledge to refresh your memory.
(You can download more fitness exam questions below to help you with your revision).
Let’s start by unpicking the above mock question and extract the keywords.
Keywords include:
- “Synergist muscle”
- and “lying Hamstring curl”.
What is a Synergist Muscle?
Synergist muscles act around a moveable joint to produce motion.
Similar to or in concert with agonist muscles.
They often act to reduce the excessive force generated by the agonist muscle.
Now a NEW keyword appears, “agonist muscles” which is another name for the Prime Mover of the exercise
Now we can be sure to categorize Synergist and agonist together.
What is the difference between Agonist and Antagonist muscles?
You know that all muscles work in pairs.
So the agonist muscle (prime mover) must also have an antagonist muscle to make up its functional muscle pairing.
Remember all muscles are attached to bones by tendons. Muscles must cross at least one or more joints and muscles contract to move our bones by pulling on them.
However, muscles can only pull; they cannot push.
This is why they work a joint in pairs.
One muscle of the pair contracts to move the body part,
the other muscle in the pair then contracts to return the body part back to the original position.
Muscles that work like this are called antagonistic pairs.
In an antagonistic muscle pair,
as one muscle contracts, the other muscle relaxes or lengthens.
The muscle that is contracting is called the agonist
and the muscle that is relaxing or lengthening is called the antagonist.
How to remember which muscle is the agonist in an exericse?
It’s the one that’s in ‘agony’ when you are doing the movement as it is the one that is doing all the work.
For example,
when you perform a bicep curl the biceps will be the agonist as it contracts to produce the movement,
while the triceps will be the antagonist as it relaxes to allow the movement to occur.
The final thing to add before we return to the mock question above.
Whenever you have an agonist, antagonist, and synergist muscle… you must also have a “Fixator” muscle.
A fixator muscle serves to stabilise the joint or part of the body that is moving.
It allows the agonist muscle to work effectively by stabilizing the origin.
In summary:
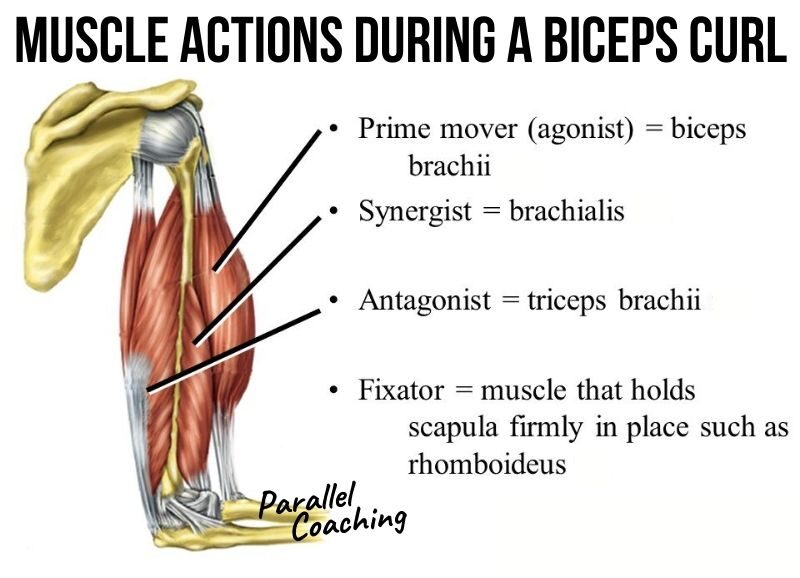
- Agonist = Prime mover
- Antagonist = opposing muscle to prime mover
- Synergist = assisting muscle to prime mover
- Fixator = stabilising muscle to prime mover
What is the Synergist Muscle in the Lying Hamstring Curl?
You are looking for the assisting muscle in the lying hamstring curl.
As you can see in the image below. Your client lies in a prone position (face down). The upper body and hips remain fixed in place. And the only joint to move is the knee joint (Hinge Joint).
The front of the upper thigh (the quadriceps) remains in contact with the machine at all times. And the knee joint pivots on the medial-lateral axis.
Aka.in line with the little red dot often found on this machine to guide the position of the knee.
As the client contracts their hamstring (the prime mover) we can recognise the antagonist muscle as the quadriceps being opposite.
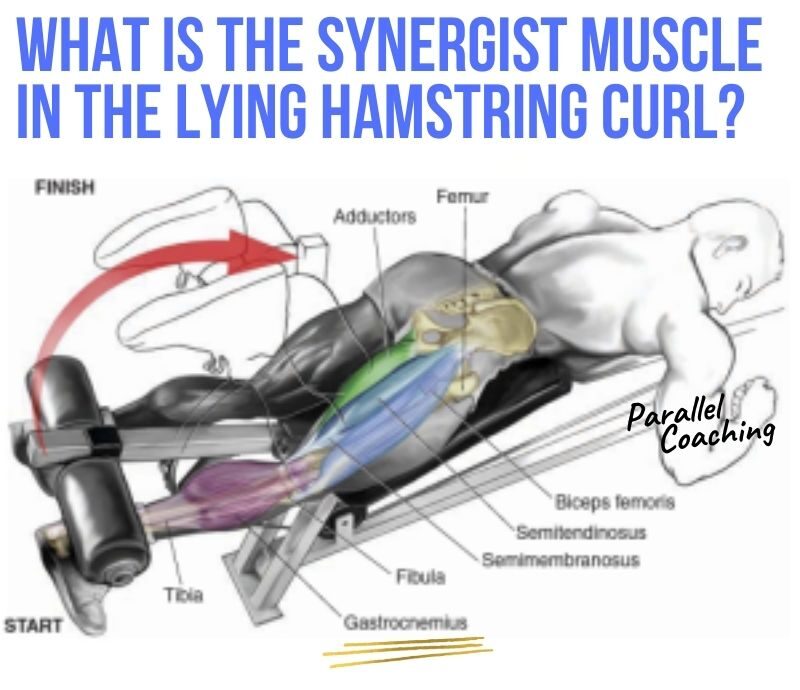
Next… fixator muscles around the hips, knee, and ankle are hard at work to stabilise key joints. Maintaining good posture and position throughout.
So the main joint working is the knee.
We know the hamstrings cross the knee and attach to the tibia, fibula.
This is key to further unpicking the mock question and picking the CORRECT answer:
Which is the Gastrocnemeus, the synergist muscle.
Remember from above… the synergist muscle is the assisting muscle to the prime mover.
With this in mind, we need to think about what other BIG muscles cross the knee on the back of the leg.
Leading you to hopefully pick the Gastrocnemuoues (the calf)
The Gastrocnemuoues originates on the femur and inserts on calcaneus via calcaneal tendon.
Its main role is to plantarflex the ankle however, it assists the hamstring due to it crossing the knee.
This also brings us to a conclusion…
More goes into planning than perhaps you first thought.
You need to understand what joints are working and what muscles are engaged and the role they play.
My hope is… the recognition that all planning is underpinned by sound anatomical and physiological knowledge.
If you know what your client’s goals are, you can recognise what anatomical and physiological changes must take place.
Final message…
we are never training exercises.
We are training the body to adapt anatomical and physiological, brought about by the stimulus of training.
Now you are familiar with the synergist and agonist muscles… test yourself on the following 3 mock questions.
Test your knowledge with today’s body in motion mock questions:
[NOTE: The answers are below the 3rd questions]
Q1: What is the agonist muscle in a Press Up?
A. Pectoralis Major
B. Triceps
C. Trapezius
D. Latissimus Dorsi
Q2: What is the synergist muscle in the Seated Row?
A. Trapezius
B. Pectoralis Major
C. Biceps Brachii
D. Biceps Femoris
Q3: If the Rectus Abdominus is the agonist in the abdomial curl, what is the name given to the Erector Spinae ?
A. Agonist
B. Antagonist
C. Synergist
D. Fixator
Answers to the mock questions are :
Question 1= A, Question 2 = C, Question 3 = B
If you want more mock questions like this, then you can download more Free Mock Questions: DOWNLOAD NOW
How to learn orgins and insertions?
Learn, Revise & Remember All 50 Muscles In The Level 3 Anatomy & Physiology Exam.
(and the BEST part…You can do all this in as little as 5-minutes a day)
Each flashcard gives you a clear image and six clear muscle facts:
- Name and Location
- Origin and Insertions
- Muscle Actions
- Joints Crossed
- Primary Planes Of Movement
- Exercise Examples

Dedicated to More
Hayley “Synergist Muscle” Bergman
Parallel Coaching
P.S. You can also find us on the following platforms:
Instagram: Follow Now
Facebook: Like Our Page
Twitter: Tweet Us
YouTube: Subscribe Here
More Circulatory System Blogs: HERE
More Muscle Revision Blogs: HERE

