This blog will teach you about Actin and Myosin and answer “how does a muscle contract?” in preparation for your Level 2 Anatomy exam.
You’ll discover:
- Why FitPros find Actin and Myosin hard to revise
- 3min Video Tutorial explaining how does a muscle contract?
- What are Actin and Myosin?
- How does a muscle contract?
- What is the sliding filament theory?
- How to learn with simplicity for the rest of the modules
- Three Example Mock Question about muscle contractions and muscle contractions
Why FitPros find Actin and Myosin so hard to revise
Understanding how muscles contract is notoriously claimed to be one of the hardest modules within the Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology syllabus, so you are not alone if you find this area difficult to understand.
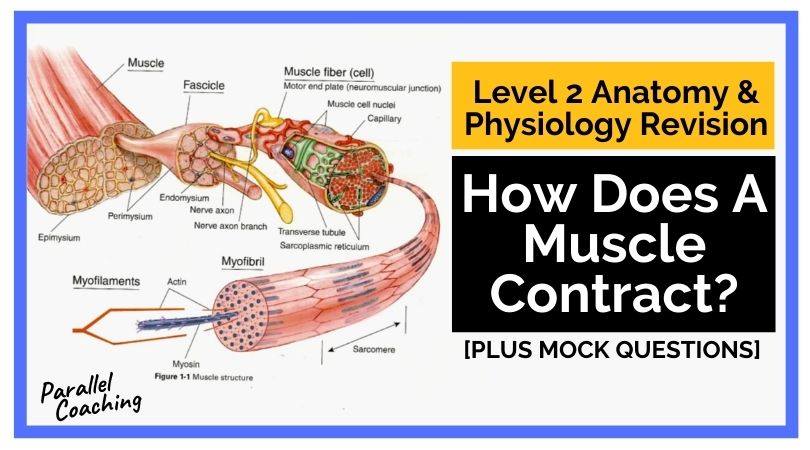
Although we can see and feel our muscles move, it is hard to picture that this is not just a solid lump of muscle, but in fact, is made up of tiny striations and microscopic protein filaments.
Although you might not be explaining about Actin and Myosin to your clients, the knowledge of this is foundational and absolutely crucial.
It allows us to understand the demand and stress we place on the muscles during exercise and to understand what is happening on every contraction.
WATCH 3 min: How Does A Muscle Contract?
How does a muscle contract?
To understand muscle structure and contraction, we need to look at it on a microscopic level
There are two types of small contractile proteins, these are collectively called myofilaments:
Actin is the Thin myofilament and
Myosin is the Fat myofilament with the golf club heads.
These two myofilaments connect at cross bridges and pull together. This is a concentric contraction, with the muscle getting shorter.
They can also lengthen under contraction which is an eccentric contraction.
In summary
- A muscle contracts via a series of tiny myofilaments pulling across each other
- You need to know about Actin and Myosin for your exam
- You can simplify and easily with our video tutorials
- Here’s what Lydia had to say about the A&P Revision Bootcamp
I can’t recommend Parallel Coaching enough their learning material is fantastic and definitely was a huge factor in me passing my A&P level 3.
Lydia
Test your knowledge with today’s mock questions:
[NOTE: The answers are below the 3rd question]
1.What is the name given to the thin myofilament?
A – Sarcomere
B – Actin
C – Myosin
D – Myofibril
2. What is the collective name given to Actin and Myosin?
A. Myofibril
B. Myofilament
C. Fascicle
D. Actin
3. What name is given to a contraction when the muscle is shortening?
A. Myostatic
B. Isometric
C. Eccentric
D. Concentric
What’s the CORRECT answer?
Answers to the mock questions are :
Question 1= B, Question 2 = B, Question 3 = D
If you want more mock questions like this, then you can download more Free Mock Questions: DOWNLOAD NOW
Need More Help with your Level 3 Anatomy Revision?
or Trainee FITPROS Taking Their L3 Anatomy & Physiology Exam.
Learn, Revise & Pass Your Level 3 Anatomy & Physiology Exam In Under 10-hours
(Without Having To Spend Hours Revising Or Feeling Overwhelmed)
If you want to get your revision structured, learn everything you need to know and feel confident on exam day, then click the link below:
https://courses.parallelcoaching.co.uk/products/level-3-anatomy–physiology-revision-bootcamp

Dedicated to More
Hayley “Actin and Myosin: How Does a Muscle Contract” Bergman
Parallel Coaching
P.S. You can also find us on the following platforms:
Instagram: Follow Now
Facebook: Like Our Page
Twitter: Tweet Us
YouTube: Subscribe Here
More Muscle Contraction Revision Blogs: HERE